| iPsychology
|
|
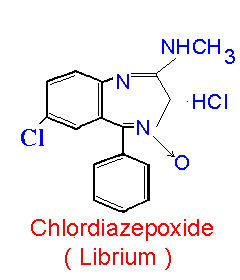
Chlordiazepoxide ( Libritabs, Librium )
Chlordiazepoxide ( Libritabs, Librium ) was the first antianxiety agent ( benzodiazepines. ) Used primarily for relief anxiety. It may also be used to treat symptoms of acute alcohol withdrawals. Sometimes given before surgery. Symptomatic relief of mild anxiety and tension and for reduction of tension states that may accompany muscle spasm. As an adjunct in tension states associated with insomnia, pre and postoperative apprehension, tension headache, premenstrual tension and stress, and functional gastrointestinal, cardiovascular, gynecological, and dermatological disorders with an emotional overlay. Chlordiazepoxide ( Libritabs, Librium ) may be useful in the alleviation of alcohol withdrawal syndromes, although drug dependence may result, substituting for alcohol dependence. Chlordiazepoxide ( Libritabs, Librium ) may also reduce anxiety associated with psychosis, but is not a specific management of psychosis. Chlordiazepoxide ( Libritabs, Librium ) is indicated for the relief of acute agitation and hyperactivity (e.g., alcoholism, anxiety, hysterical and panic states, drug withdrawal symptoms) when rapid action is required or oral administration is not feasible. Strengths:
Dosages: Actual dosage must be determined by a physician. Oral:
Problems with:
Take With: Water, Full Benefits In: 1 to 3 days. Missed Dose(s): If within one hour take, if over an hour skip and then continue on your normal schedule. Never Take a Double Dose. If Stop Taking: Do not stop without consulting your physician . Overdose: Drowsiness, ataxia, coma, confusion, diminished reflexes. Depression of the cardiovascular and respiratory centers may occur. Warnings
Narcotics may increase the sedative effects of this drug. Do not take other sedative, benzodiazepines, or sleeping pills with this drug. The combinations could be fatal. Do not drink alcohol when taking benzodiazepines. Alcohol can lower blood pressure and decrease your breathing rate to the point of unconsciousness. The habit-forming potential is high. It is possible to become dependent in only two weeks. This drugs should not be taken for more then four weeks on a regular basis ( Yudofsky, Hales and Ferguson ). If you have been taking this drug regularly for three or more weeks then do not stop taking this drug abruptly, this could cause psychological and physical withdrawal symptoms. Do not take this drug if you are pregnant. Do not take this drug if planning to become pregnant. Do not take if you are breast-feeding. Do not give this drug to anyone under the age six. Only use drug in small doses if over sixty with very close monitoring. Do not use if: You had negative reactions to other benzodiazepines, if you have a history of drug dependence, if you have had a stroke, if you have multiple sclerosis, if you have Alzheimer's disease, if you are seriously depressed or if you have other brain disorders. Chlordiazepoxide ( Symptoms or Effects ) Common:drowsiness, fatigue, light-headedness, or speech problems. Less common: abdominal cramps, constipation, dry mouth, hyperventilation, blurred vision, nausea, chest pain, change in sex drive, confusion, headache, change in appetite, insomnia, unusual dreams, change in salivation, low blood pressure, racing heartbeat, fainting, nasal congestion, difficulty urinating, sweating, weight change, skin irritation, twitching or tremors, nervous or anxious state, sun sensitivity, respiratory infection, memory impairment, menstrual difficulties, and loss of coordination. Rare: difficulty concentrating, slurred or unusual speech, double vision, fear, altered sense of taste, lack of inhibition, muscle cramps or spasms, urination problems, tingling, incontinence, warmth, weakness, change in muscle tone, or yellow eyes and skin. See physician always: Abdominal cramps, blurred vision, dry mouth, racing heartbeat / palpitations, shaking / slurred speech, urination problems, convulsions, hallucinations, memory loss, trouble breathing, staggering / trembling, headache or confusion., memory loss, confusion or staggering / trembling. Stop taking and see physician NOW: Convulsions, hallucinations, trouble breathing, hyperexcitement, muscle spasm, anxiety, hallucinations, rage or other hostile behavior, tremors, insomnia, sleeping difficulties or overstimulation. Librium has been known to interact undesirably with certain medical conditions. Tell your doctor if you have, or have a history of, any of the following conditions:
|